* Trie
컴퓨터 공학에서 trie, 혹은 prefix tree라 함은, 주로 스트링을 가지는 동적 셋 혹은 연관 배열을 저장하는데 사용되는 정렬된 트리 자료구조를 의미한다. 이진 검색 트리와는 다르게, 트리상에서의 노드들은 그 노드와 연관된 키를 저장하지 않는다. 이 대신, 트리상에서의 위치가 현재의 키를 나타낸다. 특정 노드의 모든 후손들은 그 노드에서와 동일한 prefix를 가지며, 루트 노드는 빈 문자열을 갖는다. 값은 모든 노드에서 존재하는 것이 아니고, 말단 노드(leaves) 혹은 특정 키에 해당하는 내부(inner) 노드에서만 존재한다. prefix tree의 공간사용을 최적화 하 위하여, compact prefix tree가 구상되었다. trie라는 단어는 reTRIEval이라는 단어에서 유래하였다. 이 단어를 만들어낸 Edward Fredkin은 이 단어를 'tree'와 동일하게 발음하지만, 다른 이들은 이것을 'trai'로 발음한다.
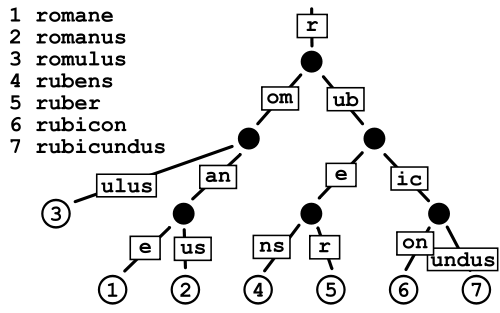
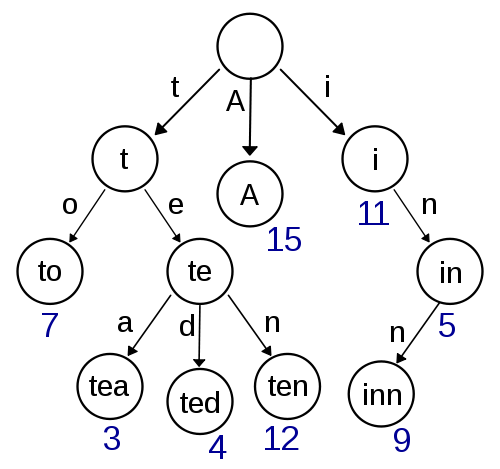
TRIE를 왜 사용해야 하는가?
많은 양의 텍스트정보를 빠르고 효율적으로 검색하기 위해
그래서 Trie는 사전 혹은 인터넷 자동완성의 retrieval을 효과적으로 할 수 있는 자료구조이다.
TRIE 특성을 간단하게 말하자면...
초반부에서도 언급했든이 TRIE란 명칭은 TREE RETRIEVAL 에서 나왔다. 가장 대표적인 특성은 키워드 정보는 마지막 노드만 가지고 있고 나머지 노드들은 정보는 없고 링크만 가지게 된다.
다음 코드는 부족한 부분이 많은 코드지만, 트라이 자료구조를 이해하시는데 조금이나마 도움이 되었으면합니다.
[코드]
|
Trie.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230 | package trie;
/*
* Java로 Trie구현
*/
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* 트라이 클래스 정의
*/
public class Trie {
private TrieNode root;
/* Constructor */
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode('\u0000'); //루트 노트생성.
}
/**
* Function name: insert
* 추가
*/
public void insert(String word) {
if (search(word) == true) return;
TrieNode current = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray() ) {
TrieNode child = current.subNode(ch);
if (child != null) {
current = child;
}
else {
current.childList.add(new TrieNode(ch));
current = current.subNode(ch);
}
current.count++;
}
current.terminal = true;
}
/**
* Function name: search
* 검색
*/
public boolean search(String word)
{
TrieNode current = root;
//문자열을 문자 배열로 쪼개서 차례대로 비교
for (char ch : word.toCharArray() ) {
if (current.subNode(ch) == null) return false; //해당 문자의 노드가 없으면 false리턴
else current = current.subNode(ch);//해당 문자가 존재하면 현재 노드에
//서브 노드 저장해서 단계별로 내려감
}
if (current.terminal == true) return true; //현재 노드가 단어의 끝인지 검사
return false;
}
/**
* Function name: remove
* 제거
*/
public void remove(String word) {
if (search(word) == false) {
System.out.println(word +"는 존재하지 않는 문자열입니다.\n");
return;
}
TrieNode current = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
TrieNode child = current.subNode(ch);
if (child.count == 1) {
current.childList.remove(child);
return;
}
else {
child.count--;
current = child;
}
}
current.terminal = false;
}
/**
* Function name: iterator
* Trie 에 저장된 단어 목록 Iterator타입으로 반환
*/
public Iterator<String> iterator() {
Set<String> elementsInTrie = new TreeSet<String>();
recursiveCallPrint(root, "", elementsInTrie); // 저장된 데이터를 elementsInTrie에 저장
Iterator<String> elementsInTrieSet = elementsInTrie.iterator();
return elementsInTrieSet;
}
/**
* Function name: recursiveCallPrint
*/
private void recursiveCallPrint(TrieNode currNode, String key, Set<String> elementsInTrie) {
// adding only the words
if (currNode.terminal) {
elementsInTrie.add(key);
}
LinkedList<TrieNode> children = currNode.childList;
Iterator<TrieNode> childIter = children.iterator();
String sKey = key;
while (childIter.hasNext()) {
TrieNode nextNode = childIter.next();
// 문자열 합치기 (키+문자)
String s = sKey + nextNode.nodeChar;
// 재귀 호출 (다음 노드, 키값, 저장셋)
recursiveCallPrint(nextNode, s, elementsInTrie);
}
}
/**
* Function name:printWord 콘솔화면에 저장된 데이터 출력
*/
public void printWord() {
System.out.println("▶Elements in the TRIE are :");
Iterator<String> itr = iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
System.out.println("===================");
}
}
/**
* 트라이 노드 정의
*/
class TrieNode implements Comparable<TrieNode> {
char nodeChar; //문자저장
boolean terminal; //리프 노드 여부
int count; //카운드 (해당노드 사용수)
LinkedList<TrieNode> childList; //자식 노드 리스트
/* Constructor */
public TrieNode(char c) {
childList = new LinkedList<TrieNode>();
terminal = false;
nodeChar = c;
count = 0;
}
boolean isTerminal() {
return terminal;
}
//해당 노드가 가지고 있는 자식 노드들에서 입력받은 문자가 있는지 검사
public TrieNode subNode(char nextChar) {
//System.out.println("subNode: "+nextChar);
//System.out.println("subNode: "+childList);
//Type1. 순차 검색.
if (childList != null) {
for (TrieNode eachChild : childList)
if (eachChild.nodeChar == nextChar)
return eachChild;
}
return null;
//Type2.
//이분검색(binary search) 알고리즘 적용 (childrenList의 요소가 정렬된 상태여야함)
//리스트에 들어있는 데이터 정렬.
//Collections.sort(childList);
//System.out.println(childList);
/*
int min= 0;
int max= childList.size() - 1;
int mid= 0;
while (min < max) {
mid = (min + max) / 2;
if (childList.get(mid).nodeChar == nextChar)
return childList.get(mid);
if (childList.get(mid).nodeChar < nextChar)
min = mid + 1;
else
// if (children[mid].nodeChar > nextChar)
max = mid - 1;
}
if (min == max)
if (childList.get(min).nodeChar == nextChar)
return childList.get(min);
return null;
*/
}//subNode()
@Override
public int compareTo(TrieNode o) { // 비교기준 정의
TrieNode other = o;
if (this.nodeChar < other.nodeChar)
return -1;
if (this.nodeChar == other.nodeChar)
return 0;
// if (this.nodeChar > other.nodeChar)
return 1;
}// compareTo()
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.nodeChar+"("+this.terminal+") ";
}//toString()
}//End Class TrieNode |
|
TrieTest.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39 | package trie;
/* Class Trie Test */
public class TrieTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//자료구조에 저장할 데이터
String data[] = new String[]{"abcd","abcf", "bcd","a", "bcdefg", "defg", "aac", "baz", "foo", "foobar","자바"};
Trie matcher = new Trie();
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
//배열에 있는 데이터를 trie 자료구조에 저장
matcher.insert(data[i]);
}
//trie에 있는 데이터 콘솔에 나열.
matcher.printWord();
System.out.println("=======제거========");
System.out.println("[abcd,abc,a] 제거");
matcher.remove("abcd");
matcher.remove("abc");
matcher.remove("a");
System.out.println("===================");
matcher.printWord();
System.out.println("=======검색========");
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
System.out.println("\tsearch test["+data[i]+"]:"+matcher.search(data[i]));
}
}//main
}//class |
|
|
|
|




댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기